GEI average values in relation to country income levels
The geography of inequity
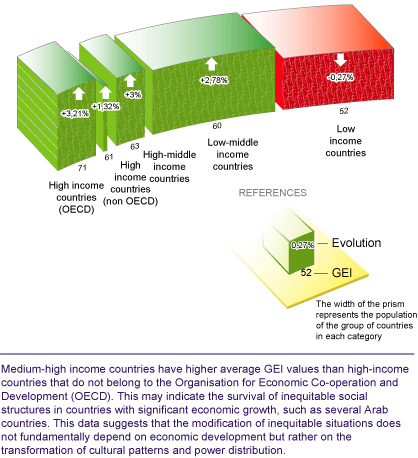
Reading Table 7 we could say that a country's wealth is related to its level of gender inequality. However, upper-middle income countries have higher average GEI values than high-income countries that do not belong to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). This may indicate the survival of inequitable social structures in countries with significant economic growth, such as several Arab countries. This data suggests that the modification of inequitable situations does not fundamentally depend on economic development but rather on the transformation of cultural patterns and power distribution.
GEI average values in relation to country income levels
|
Groups of countries by income |
IEG |
|
High income countries |
73 |
|
Upper-middle income countries |
64 |
|
High income countries (non OECD) |
62 |
|
Lower-middle income countries |
60 |
|
Low income countries |
54 |

